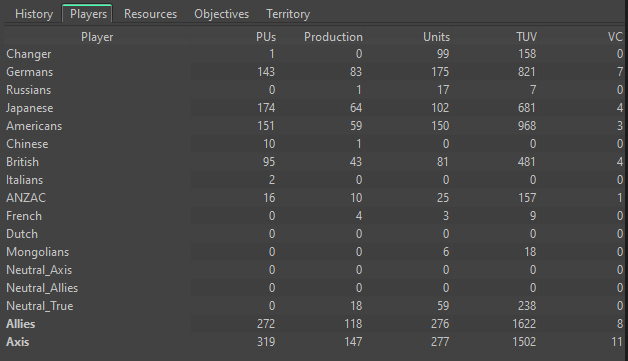
@VictoryFirst
Game #1 Victory First vs Panzerstahl-Helm
Game: 1940
Axis: VictoryFirst
Allies: Panzer
Game Thread: https://www.axisandallies.org/forums/topic/40900/1-victoryfirst-axis-vs-panzerstahl-helm-allies-g40-house-rules-expansion-by-the-captain/12
Final Save: g13-final_endsieg.tsvg
It’s been a while since the game, but I’d still like to give you the match report.
Disclaimer - the report was created by AI by giving the turn summary to the bot as fodder. I added a few comments of my own in italics, as well as the world map at the end of every 2 turns after the France turn.
I also created a report for each nation and faction.
Spoiler - Congratulations to VictoryFirst on his well-deserved victory and thanks for the great game! That was brilliantly executed master-plan!
Round 1: Initial German Offensive (Late 1940)
Germany launched a large-scale multi-front offensive, concentrating forces in Western Europe. Major territorial gains included the capture of France, Southern France, and Yugoslavia. German naval forces engaged British ships in the Atlantic, with mixed results, while land operations succeeded with the use of air and armored divisions. Casualties were moderate, but German positions were solidified across key European territories.
Round 2: Axis Expansion
German forces reinforced their positions in Europe and advanced through Bulgaria, continuing their dominance on land. U-boat wolf packs continued their operations in the Atlantic, while ground forces stabilized fronts in France and Yugoslavia. Japan secured significant victories in China and Southeast Asia, further extending Axis control in the Pacific. Italy made gains in North Africa, expanding their territorial holdings.
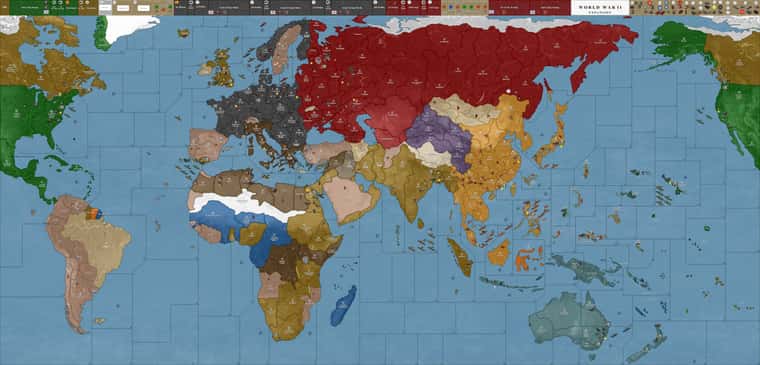
Round 3: Allied Resistance and Naval Skirmishes
The Axis powers strengthened their positions but faced growing resistance from the Allies. German naval forces clashed with British and American fleets, suffering losses, but maintaining control over strategic sea zones. On land, Germany prepared for future offensives by consolidating forces in Poland and Romania. Japan continued its unchecked expansion in the Pacific, while Italy’s control over North Africa tightened.
Round 4: Axis Fortifications
Germany reinforced its naval presence in the Atlantic and Mediterranean, deploying additional U-boats. On land, German forces built defensive fortifications across Southern Europe, focusing on maintaining their gains. Japan continued its push across Southeast Asia, while the Allies began mounting more effective counter-naval operations.
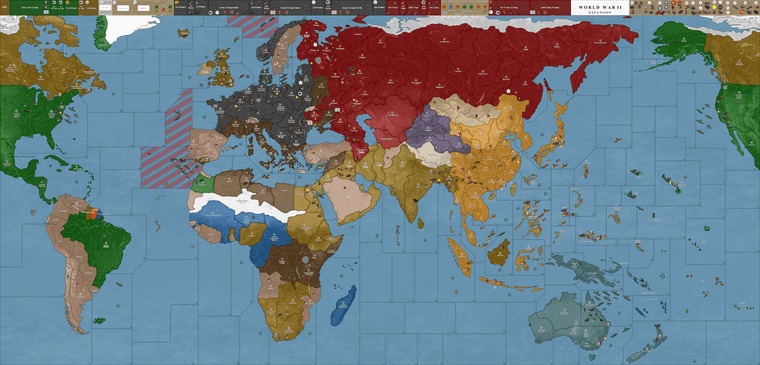
Round 5: Naval Engagements and Italian Advances
Naval engagements intensified as German U-boats continued to disrupt Allied shipping. Meanwhile, the Italian Army expanded its hold on North Africa, maintaining pressure on British forces. Japanese forces further strengthened their control over the Pacific, meeting limited resistance as Allied forces struggled to regroup.
Round 6: Allied Naval Counteroffensive
The Allies gained momentum at sea, neutralizing several German wolf packs. Despite this, Germany held firm on land, fortifying positions in Europe. Japan retained control over key Pacific territories, while ANZAC and American forces prepared for counteroffensives. Italian operations in North Africa continued, but Allied resistance stiffened.
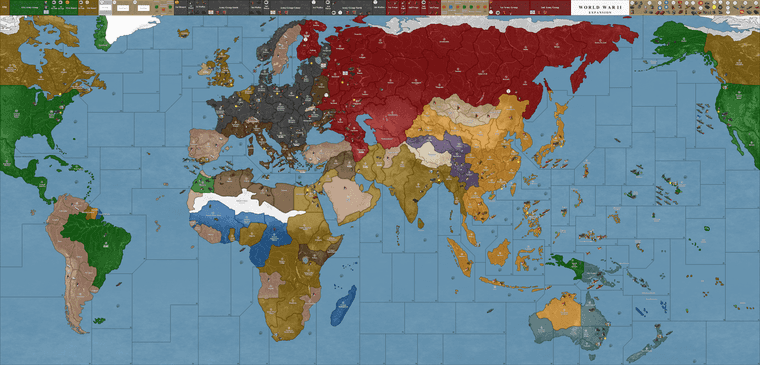
Round 7: German Technological Expansion
Germany focused on advanced technological production, including mechanized and armored divisions, and maintained pressure in naval battles. U-boat forces disrupted Allied convoys, but the balance of naval power began to shift. Japan reinforced its Pacific territories, ensuring dominance in the region.
Round 8: Stalemates and Increased Resistance
Germany ramped up air and tank production while reinforcing Southern Europe. Naval operations continued with mixed success as the Allies gained ground. In the Pacific, ANZAC forces made incremental gains, weakening Japan’s grip on key islands. Italy’s defense in North Africa remained strong, but cracks started to appear.

Round 9: Axis Defensive Strain
Allied forces secured major naval victories, reducing the effectiveness of the German U-boat campaign. German forces, stretched thin, struggled to maintain control over strategic sea zones. In the Pacific, ANZAC forces liberated several islands, weakening Japanese dominance. Axis defenses remained strong, but signs of strain emerged.
Round 10: Axis Reinforcement and Italian Collapse
Germany took control of Italy and fortified Southern Europe. Italian forces began to collapse under Allied pressure, but German reinforcements bolstered the region. U-boat operations continued, though Allied naval forces improved their effectiveness. On the Eastern Front, the German was able to land a heavy effective hit against the Russian and the 2nd Panzer Army as well as the 3rd Corps and 4 fighter squadrons were crushed in Kazakhstan! After this loss and the conquest of extensive areas in the north and east of Moscow, the Russians were encircled by the Axis forces. In the Pacific, ANZAC continued its advance, further strengthening control over the region.
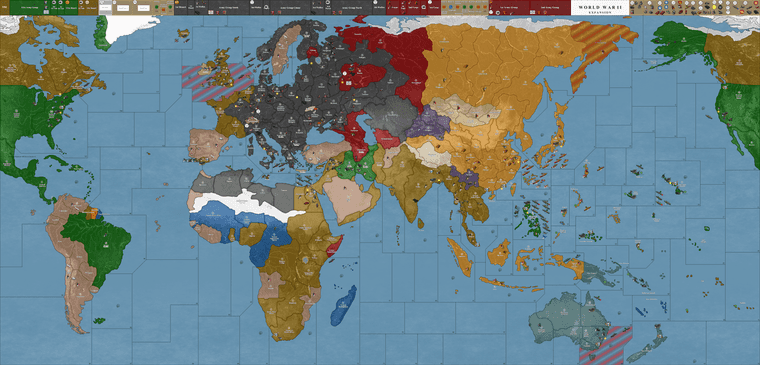
Round 11: Allied Naval Victories and Axis Resilience
The Allies continued to erode the Axis naval presence, successfully countering U-boat operations. German forces remained entrenched in Europe but faced growing Allied pressure. <FONT color=red>Nevertheless, the encirclement around Moscow was held and even strengthened. The onion domes on Red Square could already be seen with the naked eye by the German units. The storming of the Russian capital was only a matter of time! Japan struggled to maintain its hold on the Pacific as ANZAC and American forces gained ground. Italy’s military efforts weakened further under sustained Allied attacks.
Round 12: Allied Counteroffensives
Germany fortified its positions in Europe, deploying new U-boats and reinforcing Southern Italy, but faced increasing difficulty holding sea zones. Allied forces made progress in the Pacific, weakening Japanese defenses. Italy’s defensive capabilities continued to deteriorate, while ANZAC solidified control over critical territories.

Round 13: Axis Stretched Thin
All available German troops with a total strength of
1 ArmyGroupActive
1 German_Hvy_Bmbr
2 LuftwaffeAces
1 Panzer_General
1 Panzer_General3
3 Panzer_Grndrss
1 Weapons_Army
1 Weapon_Colonel
16 armour
3 artilleries
5 bombers
1 elite
8 fighters
13 infantry
1 mech_infantry
1 tactical_bomber
2 weapon_infantrys
and 2 waffen_panzers
faced an inferior Allied force of
1 FighterAceUSA
6 usa_fighters
Russians 1 ArmyGroupActive
1 FighterAce
1 FlakTower
1 Soviet_Commisar
1 Soviet_Commisar_2
1 Tank_General3
6 aaGunNOs
16 armour
1 elite
5 guard_infantrys
and 1 tactical_bomber
opposite. After a short but tough battle, the Russian lines were broken through and completely destroyed in a coup de main. The Russian Empire became history! Allied naval forces continued to gain dominance in both the Atlantic and Pacific. German U-boat fleets suffered heavy losses, weakening their ability to disrupt Allied shipping. Japanese forces, though still strong, began to lose critical islands to ANZAC and American advances. Italy remained under German control but was increasingly vulnerable to Allied offensives. *In a final joint attempt by the Anglo-American allies to bring the German Reich to its knees after all, the total loss of British landing troops at the gates of Berlin was a failure. *
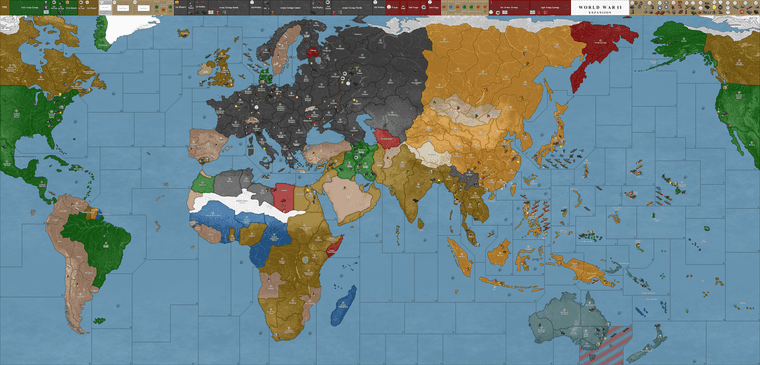
Operational Report: Summary by Nation
Germany
Rounds 1-2: Germany initiated a swift and aggressive campaign across Western Europe, achieving remarkable victories by capturing France, Southern France, and Yugoslavia. The German military utilized their air superiority and naval forces effectively, establishing dominance in the Atlantic.
Rounds 3-4: Following their initial successes, German forces fortified their positions in occupied territories and increased U-boat production. Naval engagements with British forces yielded mixed results, but the ground campaign remained strong.
Rounds 5-6: Germany focused on technological advancements, enhancing their mechanized divisions and heavy tank production. Despite successful U-boat operations, the Allies began to improve their counter-naval tactics, leading to increased losses for German shipping.
Rounds 7-9: As the war progressed, the German military faced challenges, particularly with the strain of prolonged engagements. They prepared for a significant campaign against the Soviet Union, known as Operation Barbarossa, which would see them invade Russia in a bid to secure vast territories.
Rounds 10-14: Germany successfully executed Operation Barbarossa, rapidly advancing into Soviet territory and capturing significant areas, including major cities. The initial campaign met with success, but as winter set in and Soviet resistance intensified, supply lines became overstretched. Despite early victories, the harsh conditions began to impede their progress, ultimately leading to a protracted conflict on the Eastern Front.
Italy
Rounds 1-2: Italy supported Germany’s advances in North Africa, achieving early successes but struggled with logistics and troop morale, relying heavily on German military support.
Rounds 3-4: The Italian military faced increasing pressure from Allied forces, particularly in North Africa, leading to heavy casualties and revealing significant vulnerabilities.
Rounds 5-6: As the situation deteriorated, Italy’s reliance on German support grew. Continued Allied offensives resulted in significant losses, contributing to Italy’s political instability.
Rounds 7-9: Political turmoil led to Italy’s collapse, and Germany took full control, integrating Italian forces into their command structure and solidifying their position in Southern Europe.
Rounds 10-14: Under German control, the Italian military operated primarily in support of German objectives. Allied advances in North Africa and the Mediterranean continued to threaten their positions.
Japan
Rounds 1-2: Japan pursued aggressive territorial expansion across Southeast Asia, achieving significant gains with minimal resistance, and establishing dominance in the Pacific.
Rounds 3-4: Continued military operations allowed Japan to fortify captured territories, although growing Allied resistance began to challenge their military efforts.
Rounds 5-6: Japan maintained military strength but faced increasing pressure as Allied forces regrouped and launched counteroffensives, which began to erode their control.
Rounds 7-9: Japanese operations encountered setbacks due to coordinated Allied attacks, leading to losses in naval engagements and the threat of losing critical territories.
Rounds 10-14: As ANZAC and American forces gained momentum, Japan struggled to maintain control over its acquisitions. Significant losses in naval battles threatened their dominance in the Pacific.
Allied Nations (ANZAC, United Kingdom, United States)
Rounds 1-2: The Allies faced early setbacks due to Axis expansion but worked to regroup and prepare for counteractions against the advancing Axis forces.
Rounds 3-4: The Allies mounted effective naval operations against German U-boats while supporting ANZAC forces in the Pacific, leading to improved coordination and strengthened positions.
Rounds 5-6: The Allies successfully neutralized several German U-boats and made considerable gains in the Pacific, regaining control of strategic territories from Japan.
Rounds 7-9: With increasing cooperation, the U.S. ramped up military production, deploying more naval assets. ANZAC and American forces achieved critical victories, reversing the tide against Japanese expansion.
Rounds 10-14: As Germany captured significant territories in Russia, the Allies maintained pressure on Axis forces, effectively neutralizing U-boat threats and liberating territories in the Pacific. The Allies prepared for further offensives, exploiting Axis vulnerabilities and the overextended German supply lines in Eastern Europe.
Summary end of the game: